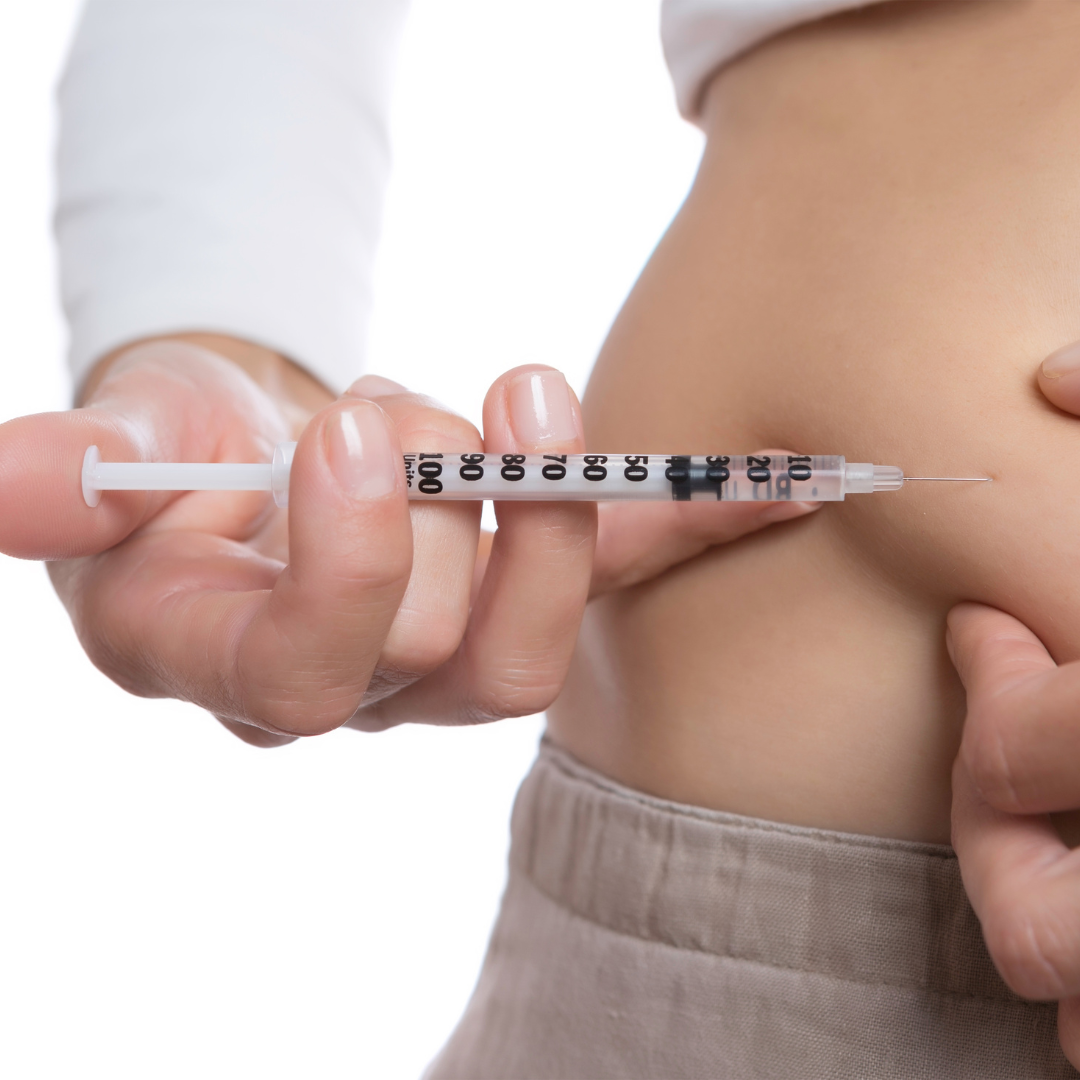
Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is a medication approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and used off-label for weight loss. Like any medication, it can have side effects. Most are mild and manageable, but some may require medical attention.
Here’s a breakdown of common Mounjaro side effects and Cost
(سعر ابر مونجارو) and tips for managing them:
✅ Common Mounjaro Side Effects
These are the side effects most frequently reported, especially when first starting or increasing the dose:
1. Nausea
-
Why it happens: Slower stomach emptying (a key mechanism of the drug).
-
Management tips:
-
Eat smaller, more frequent meals.
-
Avoid high-fat or greasy foods.
-
Stay upright after eating.
-
Ginger tea or ginger supplements may help.
-
2. Vomiting
-
Why it happens: Can be a result of severe nausea.
-
Management tips:
-
Try nausea prevention strategies.
-
Stay hydrated with electrolyte drinks.
-
If vomiting persists, talk to your doctor about lowering your dose.
-
3. Diarrhea
-
Why it happens: Gastrointestinal system adapting to the medication.
-
Management tips:
-
Stay hydrated.
-
Avoid caffeine, dairy, and high-fat foods.
-
Eat bland foods (BRAT diet: bananas, rice, applesauce, toast).
-
4. Constipation
-
Why it happens: Slowed digestion.
-
Management tips:
-
Increase water intake.
-
Add fiber to your diet gradually.
-
Light exercise can help digestion.
-
Consider stool softeners or fiber supplements (e.g., psyllium).
-
5. Decreased Appetite
-
Why it happens: Mounjaro slows gastric emptying and affects hunger signals.
-
Management tips:
-
Monitor your intake to ensure you’re still getting enough nutrients.
-
Work with a dietitian if you're losing too much weight too fast.
-
6. Fatigue
-
Why it happens: Can be related to reduced calorie intake or dehydration.
-
Management tips:
-
Make sure you’re eating enough nutritious food.
-
Prioritize rest and hydration.
-
If persistent, consult your healthcare provider.
-
⚠️ Less Common but Serious Side Effects
These are rare but require immediate medical attention:
1. Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
-
Symptoms: Severe abdominal pain (especially radiating to the back), nausea, vomiting.
-
Action: Stop the medication and seek immediate medical help.
2. Gallbladder issues (e.g., gallstones)
-
Symptoms: Upper right abdominal pain, nausea after eating, fever.
-
Action: Seek medical evaluation.
3. Kidney problems
-
Symptoms: Decreased urine output, swelling, fatigue.
-
Action: Especially important to stay hydrated and monitor kidney function if you have pre-existing issues.
4. Allergic reactions
-
Symptoms: Rash, swelling of face/tongue/throat, difficulty breathing.
-
Action: Emergency medical attention is needed.
💡 Tips for Managing Side Effects Overall
-
Start low, go slow: Dose escalation (usually every 4 weeks) helps minimize side effects.
-
Stay hydrated: Especially important if experiencing GI side effects.
-
Track symptoms: Keep a journal to discuss with your provider.
-
Communicate with your doctor: Don’t suffer through side effects; they may adjust your dose or timing.
📌 When to Call Your Healthcare Provider
-
If side effects are severe or persistent.
-
If you experience signs of pancreatitis, gallstones, or kidney issues.
-
If you’re unable to eat or drink enough due to nausea or vomiting.